2. What’s new in PyMoDAQ 4
The main modifications in PyMoDAQ 4 is related to the hierarchy of the modules in the source code and the data management.
The feel and shape of the control modules and the way the DAQ_Scan work have been reworked. A new extension is introduced: the Console.
2.1. Package hierarchy
Before many modules where stored in a generic daq_utils
module. It was kind of messy and the development of much nicer code for pymo4 was the occasion to reshape the
package and its modules. Figure Fig. 2.1 shows the new layout of the package.
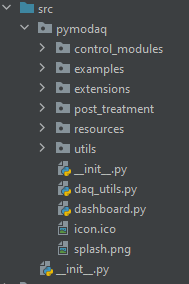
Fig. 2.1 Layout of the PyMoDAQ 4 package.
The only python file at the root is the dashboard.py that contains the code about the dashoard, the starting point of PyMoDAQ usage.
Note
There is a daq_utils.py file here as well to provide some back compatibility with pymodaq v3 but this file will soon be deprecated (when all plugins will be updated according to this tutorial)
Then you’ll find modules for:
Control modules: the
DAQ_Viewerand theDAQ_Moveand their utility modulesExample module: contains some executable code to illustrate some features
Extension module: contains the main extension of the DashBoard:
DAQ_Scan,DAQ_Logger,PIDandH5BrowserPost-Treatment modules: utilities to process PyMoDAQ’s data
Resources module: contains the UI icons, templates for configuration and presets
Utils module: contains all utility modules, see Fig. 2.2.
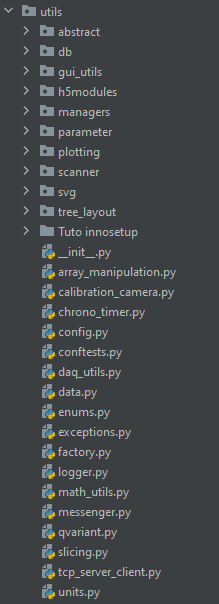
Fig. 2.2 Layout of the utils module
This last utils module contains many other module needed for PyMoDAQ to run smoothly. They can also be used
in some other programs to use their features. Below is a short description of what they are related to:
abstract: contains abstract classes (if not stored in another specific module)
db: module related to data logging towards database (postgresql for instance)
gui_utils: usefull UI widgets and related objects to build quickly and nicely user interfaces
h5modules: everything related to the saving and browsing of data in hdf5 files
managers: integrated objects managing various thing, for instance, control modules, presets, roi… In general they have a specific UI (that you can incorporate in your main UI) and the code to interact with whatever is related to it.
parameter: extensions of the pyqtgraph Parameter introducing other widgets and Parameter types. Includes also serializers from/to Parameter to/from XML
plotting: everything related to the plotting of data: including the 4 main data viewers, see Plotting Data
scanner: objects related to the DAQ_Scan defining and managing the scans. The different types of scans are defined using a factory pattern.
svg: under tests to plot svg
array_manipulation: utility functions to create, manipulate and extract info from numpy arrays
calibration_camera: utility UI to get a calibration file from a Camera compatible with pymodaq (to use real physical axes and not pixels in the data viewers). Old code, maybe to update for it to work
chrono_timer: user interface to be used for timing things, see ChronoTimer
config: objects dealing with configuration files (for instance the main config for pymodaq). Can be used elsewhere, for instance in instrument plugin
conftests: configuration file for the test suite
daq_utils: deprecated
data: module containing all objects related to Data Management
enums: base class and method to ease the use of enumerated types
exceptions: contains some shared exceptions. But exceptions should be in their related module…
factory: base class to be used when defining a factory pattern
logger: methods to initialize the logging objects in the various modules
math_utils: a set of useful mathematical functions
messenger: function to be used when one want to display messages (in the log or in popups)
qvariant: definition of a QVariant object. To be used in PySide as it is not defined there…
slicing: definition of slicing objects used in the data management to slice data
tcp_server_client: set of classes to build TCP/IP communication
units: methods for conversion between physical units (especially photon energy in eV, nm, cm, J…)
2.2. Data Management
See data management.
2.3. DAQ_Scan
See DAQ Scan.